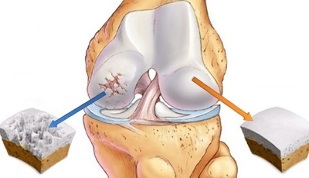
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative articular pathology, accompanied by processes of cartilage tissue dystrophy. As the disease progresses, articular bags, ligament apparatus, synovial membrane, and proximal bone structures are also involved in the destructive process.
Prevalence of osteoarthritis
Most people with osteoarthritis are the elderly. The disease after the age of 65 is not only the most commonly diagnosed joint pathology, but also the main reason for disability with subsequent disability. Moreover, in old age, mostly women are sick, but among the young, most of the sick are men.
In different countries, the incidence of osteoarthritis varies greatly. It has not yet been possible to determine the reasons for the widespread dissemination of statistical data.
Causes and risk factors
Osteoarthritis is a disease that can be primary or secondary. If there is no objective reason for the development of pathology, they speak of the primary type. If it was possible to identify the causes of osteoarthritis, they speak of the secondary type.Secondary osteoarthritis can be caused by the following negative factors:
- traumatization of articular joints of various nature (frequent falls, sprains, bruises);
- chronic congenital tissue dysplasia;
- pathological changes in metabolic processes;
- various autoimmune pathologies;
- nonspecific inflammatory processes in the joint area;
- some pathologies of the organs of the endocrine system;
- degenerative-dystrophic type processes that occur chronically;
- various diseases, accompanied by excessive mobility of the joints, accompanied by a weak ligament apparatus;
- presence of hemophilia;
- specific type of inflammatory processes.
In addition to the immediate causes, the action of which leads to the development of osteoarthritis, there are also predisposing factors that do not cause the disease itself, but may increase the risk of developing it.
These include:
- is over 55 years old;
- excess weight, due to which the load on the articular joints increases;
- Excessive load on a joint or group in case of improper sports training, specific work that requires a long stay in one position;
- history of joint surgery; inheritance
- ;
- hormonal changes in the postmenopausal female body;
- persistent hypothermia;
- untreated spinal pathologies; Insufficient intake of useful micro- and macronutrients with food.
Development Mechanism
The mechanism of development of osteoarthritis is well known. The cartilage, which ensures normal contact of the two bones, is naturally soft, without irregularities and roughness, which helps maintain normal movement in the joints. With a disease, the structure of the cartilage changes, it becomes stiff, defects appear in it, which reduce the effectiveness of natural sliding.Due to the acquired inequality, the cartilage is gradually injured, in places it begins to calcify and in places it ossifies. In this case, it is possible to separate small particles that end up in the joint fluid and can damage the surrounding tissues.
As the pathology worsens, the joint may progress to a state of chronic subluxation, which will significantly impair its motor function.
Degrees
Doctors divide osteoarthritis into three main degrees:
- grade I.It is characterized by a lack of a clear clinical picture. The patient may present with rare complaints of pain in the affected joint, but usually does not consult a physician. At the same time, there are changes in the ligament-muscular apparatus and in the articular fluid, but there are still no noticeable deformities.
- degree II.The symptoms of osteoarthritis become more pronounced. The pain is characterized as bearable, but occurs regularly. The patient goes to the doctor, after noticing a decrease in quality of life. A characteristic crack can be heard in the affected node. Changes are observed in nearby muscle structures, as nerve conduction is disturbed.
- degree III.Characterized by bold characters. The articular cartilage is very thin, cysts, foci of calcification or ossification can be found in it. The ligament apparatus becomes shorter, which leads to an increase in mobility in the affected area, which is accompanied by a restriction due to a pronounced inflammatory process. The metabolism of the surrounding tissues suffers, which can lead to muscular dystrophy.
In any case, the patient will need to clarify the diagnosis from the attending physician. This is due to the specificity of the course of the disease, which is characterized by phases of remission and deterioration, alternating alternately with each other.
Pain with disease
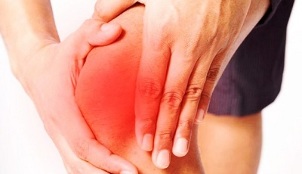
Pain in osteoarthritis is the most common complaint that patients go to the doctor. Their characteristic feature is their connection with the time of day, weather, physical activity.
In most patients, the pain is exacerbated by walking, running, or some other type of physical activity directed at the affected joint. Once the load stops, the pain gradually subsides. Their development is explained by the fact that cartilage is no longer able to perform its shock-absorbing functions.
At night, the discomfort most often appears as a result of blood clots in the veins. Another reason is the increase in intraosseous pressure during this period.
One of the main diagnostic criteria is the presence of so-called initial pain that bothers the patient at the moment when he has just started active movement. The initial pain usually subsides if physical activity continues. Their occurrence is explained by the presence of articular deposits (detritus) that irritate nerve endings. Once these deposits are removed from the nerves, the pain disappears.
Symptoms
In addition to pain, doctors identify other signs of osteoarthritis, with which pathology may be suspected.
These include:
- Pain and soft sound. Lomota appears mainly in case a person has got hypothermia. Chewing at first will be barely audible, but as the disease progresses without therapy, it will become audible to the people around.
- Decreased ability to move. At an early stage of pathology development, there is no decrease in mobility. However, the longer the disease is left untreated, the stronger the restriction of movement in the joint becomes. This is explained by the narrowing of the joint space and the spasm of the nearest muscle structures.
- Deformity of the wrist.is characteristic of the late stage of osteoarthritis, but is also an important indicator of the course of the disease. During this period, it is already very difficult to treat the disease.
Which doctor treats osteoarthritis?
Who treats osteoarthritis? In most cases, some specialists are involved in therapy. First of all, an arthrologist is involved - a specialist in joints. Furthermore, the patient will need to visit an orthopedist. If the disease is a consequence of an inflammatory process, then it is recommended to visit a rheumatologist as well.
If necessary, other specialists may be involved during the treatment period. Most often, you should turn to the services of traumatologists, physiotherapists, masseurs, surgeons.
Diagnosis
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the joints begins only after the diagnosis is confirmed and the degree of pathology is determined. First of all, the doctor interviews the patient in detail and performs an examination. The presence of characteristic complaints and deformities suggests that a disease exists.
Radiography of the affected joint is a mandatory way to confirm the diagnosis. If the disease affects the knee, then a photograph of the knee is taken, if the pathology is found on the hand, then the radiological signs of the disease are specifically sought there.
Diagnosis using radiography does not always give sufficient results to diagnose the patient. In this case, it can be sent for MRI (this will allow the assessment of the condition of soft tissues and their involvement in the pathological process) or CT (this will make it possible to draw conclusions about the condition of bones and structurescartilage, the involvement of the closest anatomical formations in the pathological process).
Treatment
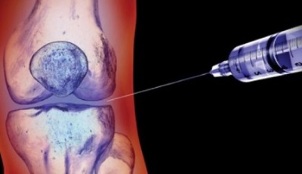
How to treat osteoarthritis of the joints? The choice of appropriate therapeutic technique depends on the severity of the symptoms and the stage of the disease.
The doctor chooses the therapy regimen after assessing the general condition of the patient and the course of the disease. Both conservative and surgical methods of treatment can be used.
Medications
How to treat a disease if it is preferable not to have surgery, but to use medication?
Conservative therapy is suitable for patients only at an early stage of pathology formation and will involve the use of three main groups of drugs:
- glucocorticosteroids- hormonal drugs that alleviate the inflammatory process during an exacerbation, are injected into the joint cavity;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,which are mainly injected and injected into muscles near the article or directly into a vein. But doctors can also recommend pills, although this option for taking NSAIDs is undesirable because of the negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract;
- Chondroprotectors- drugs of this group can reduce the destruction of cartilage tissue and regenerate, are especially effective in the early stages of disease formation.
Surgical
How to cure osteoarthritis, if the disease has gone far enough? In this case, conservative therapy will be ineffective and doctors can only recommend surgery to the patient.
Today, key replacement is performed in most cases. During surgery, the true joint is replaced with a prosthesis, which has all the functions of a healthy joint.
In some cases, palliative therapy options are offered, the main task of which is to reduce the load on the articular surfaces.
Exercise
In the early stages of the disease, it is treated not only with medication but also with physiotherapy exercises. Exercise is an important phase of therapy that helps maintain the functionality of the article and reduces the likelihood of further disease progression.
Depending on the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the patient, the set of exercises is chosen individually. The physician should consider the localization of osteoarthritis, which allows the most effective effect on the affected tissues.
Self-study without medical supervision is not recommended, especially in the initial stage. Exercises should be chosen so that they are as smooth as possible, without sudden movements.
Exercise therapy classes are effective only if the patient devotes some time to the recommended complex each day.
Traditional methods

Many people suffering from osteoarthritis refuse to use medication or surgery until the last minute. In this case, alternative medicines are used as substitutes for medicines.
The most widely used plants in therapy are:
- Kalanchoe;
- ginger;
- ferr;
- laurel leaves;
- garlic;
- cinnamon;
- ponytail and others.
They are used in the form of tinctures, decoctions, poultice on the affected area. Importers It is important to keep in mind that a complete cure of the disease using only home prescriptions is impossible. It is better if traditional therapies are combined with traditional medicines.
Prevention
What should you do to reduce the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis in old age? Simple preventative measures are available to anyone.
Recommended:
- moderate daily physical activity: walking, cycling, doing simple exercises like load, etc.
- adherence to the basic principles of a healthy diet: eat often, but little by little, avoid fast food, overeating, heavy and fatty foods, eating lots of spices;
- weight control: weight gain leads to increased stress on the joints, which can lead to osteoarthritis;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases leading to metabolic disorders;
- use of vitamin and mineral complexes in case the amount of nutrients supplied to the food is considered insufficient.
The difference between arthritis and osteoarthritis
Many people confuse arthritis and osteoarthritis because of the similarity of sound. However, these are completely different diseases.
Arthritis is not dystrophy and degeneration in the joint tissue, but any inflammatory reaction that may develop in the joint cavity, regardless of its cause. Inflammation most often affects not only the joint, but also the muscles closest to it, the bone structures and ligaments. Arthritis pain is not associated with physical exertion, it can bother the patient even at rest and there is no joint crisis at all.
In most cases, it is impossible to distinguish arthritis from osteoarthritis independently, as the main symptom is pain, and patients rarely have an idea of its features for each of the pathologies.
it is best to entrust the establishment of an accurate diagnosis to the attending physician so as not to make mistakes in subsequent treatment and prevention of the disease.
Osteoarthritis is a serious pathology that can lead to disability if the patient does not visit a doctor on time. At the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to contact a specialist to confirm the diagnosis and choose the most optimal treatment.If it is possible to catch the disease at an early stage of development, then it will certainly be possible to do it even without surgery, being limited to conservative treatment only.



































